Percentage of Female Legislators
By: V-Dem Staff
Sep 28, 2016
Across the globe there are several methods for approaching equal representation. Some political parties engage in voluntary quotas for their election lists. Some countries have laws requiring a certain percentage and ranking of female candidates in the election lists, others have reserved seats for women and some countries have no policy. How do these practices differ in their results?
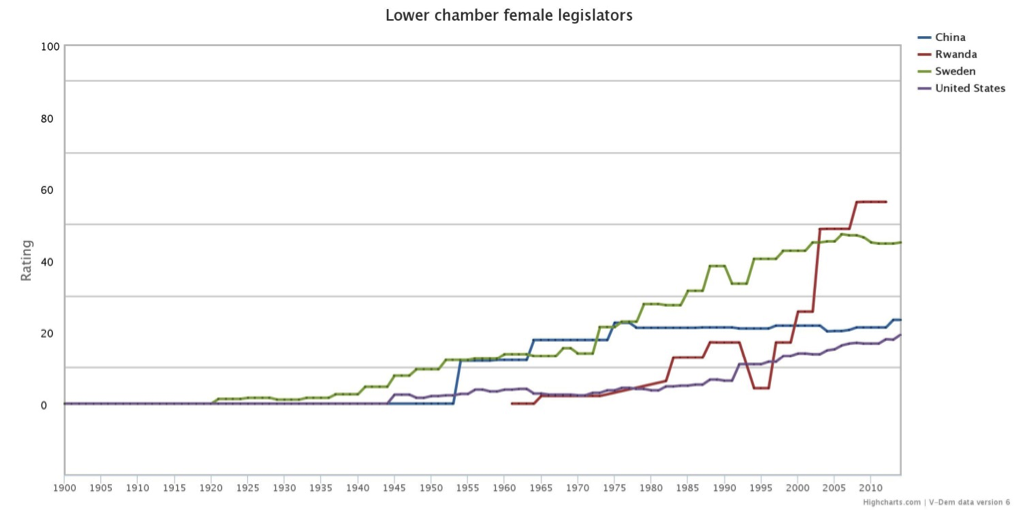
Currently, Rwanda, enforcing legislated gender quotas in its 2003 Constitution, lies at the top of its counterparts. V-Dem data for Rwanda stands at 56.3 per cent of women in the parliament.. Sweden, practicing voluntary political party quotas, has a more stable increase in the percentage of female representation. Until 2003, Sweden was almost always comfortably ahead of the other three countries with a high record of female representation. This trend could be attributed to the early adoption of voluntary quotas by the largest party in Swedish politics in 1978.
China, unlike Sweden and Rwanda, has plateaued since mid-1970s at around 21 percent. Since 2007, the Chinese legislature mandates a minimum of 22 per cent quota for female representatives. However, we see in the graph that they have had a hard time moving above the minimum level. Lastly, United States have lagged behind in terms of female representation. Currently there is no voluntary or legislated policy to increase female representation in Congress.
You can learn more about female political participation across the globe with other V-Dem indexes on v-dem.net using the online analysis tools.